Design for Mass Production (DFM):
Bridging the Gap Between Concept and Scale
In the competitive landscape of the global toy industry, the transition from a breathtaking creative concept to a profitable retail reality is governed by one critical discipline: Design for Mass Production (DFM). At Unstoyppable, we understand that a prototype is merely a proof of possibility, while a DFM-optimized design is a proof of profitability. Engineering for mass production is the strategic process of refining a product’s geometry, material composition, and assembly logic to ensure it can be manufactured at high speed with zero variance. For 2026, scalable toy manufacturing requires more than just a factory line; it requires an "industrial blueprint" that anticipates the physical stresses of injection molding and the logistical demands of global fulfillment. By implementing rigorous toy DFM principles, we enable brand owners to maintain the artistic integrity of their IP while achieving the radical efficiency necessary for reducing toy production costs on a massive scale.
Engineering for Consistency and Character Integrity
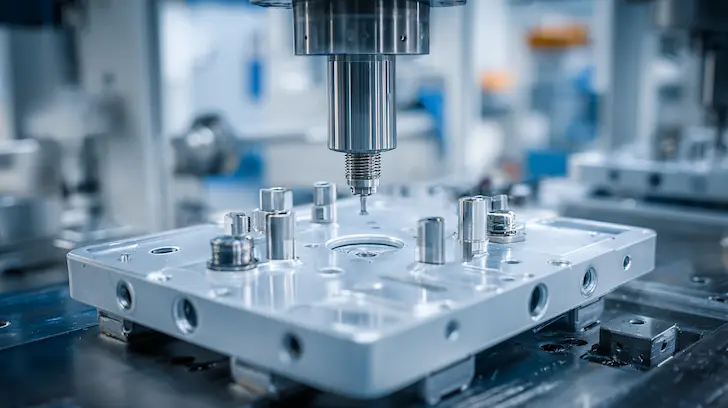
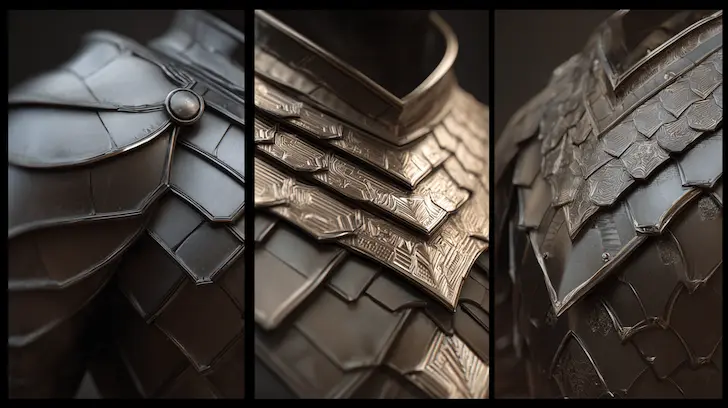
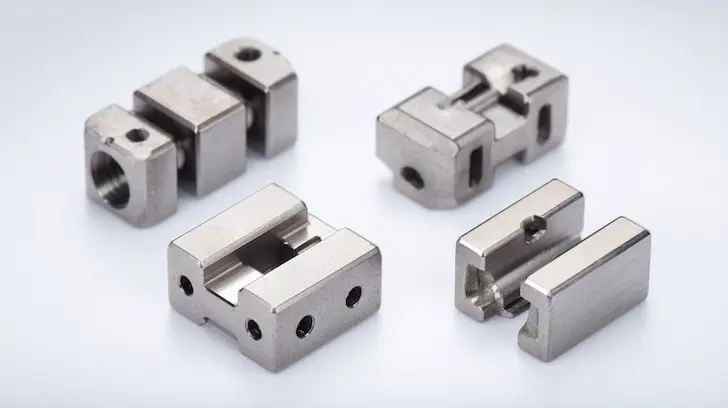
The primary goal of design for mass production toys is the elimination of production variables. When producing a single handcrafted model, an artisan can manually fix a seam or sand down a rough edge. In a run of one million units, such manual intervention is a bottleneck that destroys ROI. We focus on "tuning" the design so that the first unit off the line is identical to the millionth. This consistency is achieved by simulating the manufacturing environment during the CAD phase, ensuring that the character's iconic silhouette is structurally reinforced for high-speed oem licensed product manufacturing. By engineering reliability into the design, we protect the brand’s reputation for quality while maximizing throughput.
Speed-to-Market Through Proactive Engineering
A well-executed DFM strategy is the fastest path to retail. By identifying potential molding failures before the steel for the tool is even ordered, we shave weeks off the production timeline. Scalable toy manufacturing depends on a "right-first-time" approach. Our engineers review every undercut and parting line to ensure the mold design is as simple and robust as possible. This proactive stance reduces the need for multiple "T1" sample iterations, allowing your brand to launch with the momentum and precision that the 2026 market demands.
Managing Warping through Thermal Balance
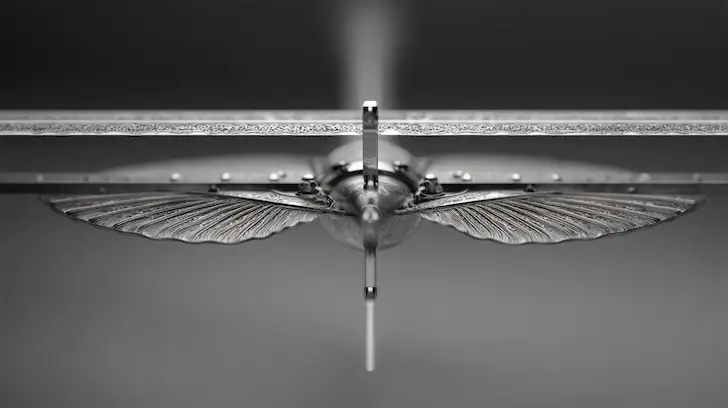
Warping is the result of internal stresses caused by non-uniform cooling. By optimizing wall thickness, we ensure a balanced thermal profile across the part. This is especially critical for flat surfaces or long, thin components like swords or wings. By maintaining the correct thickness-to-length ratios, we ensure that every component stays straight and true to the original 3D sculpt. This technical precision is what allows Unstoyppable to deliver retail-ready licensed product production that meets the highest standards of the most demanding collectors.
Transform Your Vision into a Scalable Asset
Excellence in design is only the beginning. Partner with our specialist engineering team for a comprehensive DFM audit that guarantees your IP is ready for global scale.
Hiding Technical Tapers in Creative Aesthetics
The "Special Ops" level of design for mass production toys involves hiding these necessary tapers within the character's design. Our engineers work closely with the IP style guides to integrate draft angles into natural features—such as the curve of an armor plate, the flare of a boot, or the drape of a cape. By camouflaging the engineering requirements, we provide a part that is optimized for scalable toy manufacturing while appearing completely "un-engineered" to the consumer. This seamless blend of form and function is why leading media franchises trust Unstoyppable for their most complex projects.
Part Consolidation (DFMA):
Reducing Assembly and Points of Failure
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) is the practice of simplifying a product’s structure to reduce the number of individual components. In the 2026 market, this is the most effective way of reducing toy production costs.
The DFM Advantage: Strategic design for mass production toys is the ultimate protection for your margins. By mastering wall thickness, draft angles, and part consolidation, Unstoyppable ensures your scalable toy manufacturing project is built on a foundation of industrial excellence. Don't just design a toy—engineer a global success.
Technical Optimization:
Material Selection and High-Speed Tooling Integration
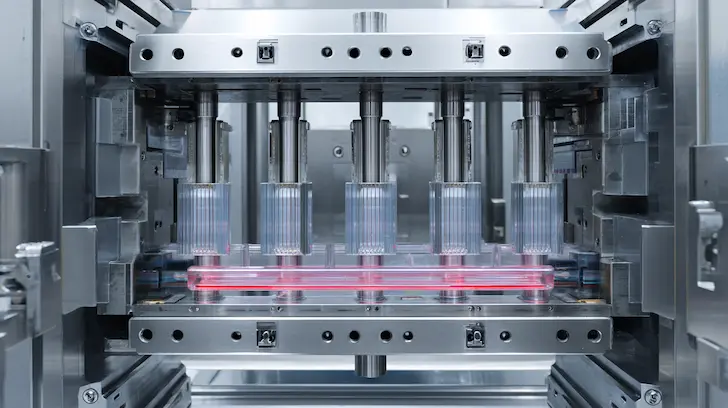
Achieving high-speed toy manufacturing at a global scale requires a seamless synergy between material science and mechanical tool design. In the DFM (Design for Manufacturing) workflow, the physical properties of the chosen resin dictate the architecture of the mold itself. At Unstoyppable, our technical optimization process ensures that the "melt-flow" of the plastic is perfectly synchronized with the geometry of the tool. This harmony is essential for maintaining injection molding DFM standards, where even a micro-second of delay in the cooling cycle or a slight mismatch in material viscosity can result in significant production bottlenecks. By integrating toy material engineering with multi-cavity toy molds, we create a robust production ecosystem that delivers thousands of identical, high-fidelity parts per hour. This level of technical precision is what allows us to transform complex IP into retail-ready licensed product production that is both cost-effective and structurally superior.
Resin Compatibility:
The Science of High-Volume Filling
The success of scalable toy manufacturing depends heavily on the "Melt Flow Index" (MFI) of the selected polymer. Our engineers select resins that are specifically formulated for high-cavitation environments.
Optimizing Melt Flow for Multi-Cavity Tooling
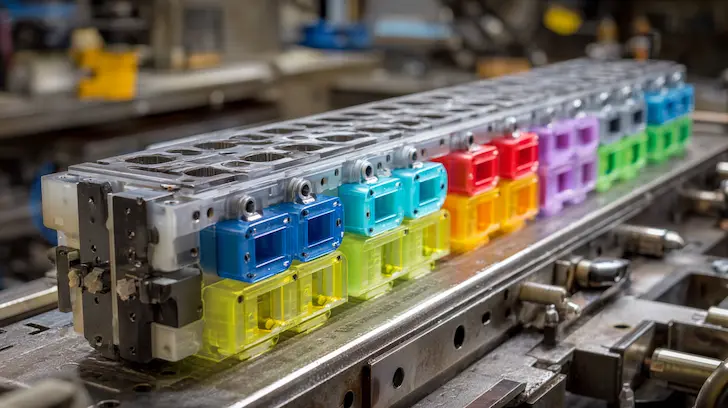
In multi-cavity toy molds, the molten plastic must travel through a complex network of runners to reach 8, 16, or even 32 cavities simultaneously. We select materials such as high-flow ABS or specialized Polypropylene (PP) that possess a high MFI, ensuring the resin reaches the furthest extremities of every cavity before it begins to solidify. This injection molding DFM strategy prevents "short shots" and ensures that every character in a high-volume run features the same crisp detail and density. By balancing the injection pressure with the resin’s viscosity, we achieve a stable, repeatable process that is the backbone of high-speed toy manufacturing.
Eliminating Manual Steps with Automated Finishing
Traditional spray painting and pad printing are often the slowest stages of toy production and the primary source of aesthetic variance. By utilizing printing film for mass production, we place a pre-printed, high-resolution film directly into the mold before injection. The molten plastic fuses with this film, creating a permanent, scratch-resistant finish that is 100% consistent across the entire production run. This technical optimization ensures that every unit matches the "Master Sample" with digital precision, providing a retail-ready licensed product production that satisfies the most meticulous brand style guides.
Enhanced Durability for Play and Display
Beyond consistency, IMD provides a level of durability that surface-applied paints cannot achieve. Because the graphic is embedded within the surface layer of the plastic, it is protected from the oils of human skin, environmental humidity, and abrasive wear. This makes it the ideal choice for character product manufacturing where the character's facial features or complex costume patterns must remain pristine after years of handling. This high-efficiency finishing method is a cornerstone of our scalable toy manufacturing services for global media franchises.
Don't Leave Your Production to Chance
Material selection and tooling strategy are the two pillars of manufacturing success. Leverage our technical expertise to ensure your next global launch is flawless.
Optimized Ejection for Rapid Cycle Times
Ejector pins are required to push the cooled part out of the mold. If poorly placed, they can distort the part or leave unsightly circular marks. Our high-speed toy manufacturing R&D team designs ejection systems that apply uniform pressure to the strongest parts of the geometry. We often integrate ejector pins into the internal structural ribs or hidden mating surfaces. This allows the mold to open and the parts to eject at maximum velocity, significantly reducing toy production costs by shortening the overall cycle time without compromising the surface finish of the custom licensed product development.
Tolerances for Mass Production:
Balancing Precision and Profitability
Establishing "Real-World" tolerances is perhaps the most important technical optimization step for long-term manufacturing success. Over-engineering tolerances can be just as damaging to a project as under-engineering them.
Technical Harmony: Successful manufacturing is the result of material science and mechanical engineering working in perfect unison. By mastering resin compatibility, in-mold decoration, and gate strategy, Unstoyppable delivers high-speed toy manufacturing that never sacrifices the artistic vision of the brand. Let us optimize your production for the global stage.
The Business Case for DFM:
Reducing Landed Costs and Ensuring Compliance
In the high-stakes world of licensed merchandise, Design for Mass Production (DFM) is far more than an engineering checklist; it is a strategic insurance policy for your brand’s profitability and reputation. At Unstoyppable, we view mass production toy ROI as a direct result of proactive design decisions made months before the first unit hits the retail shelf. By integrating toy safety DFM into the initial development phase, we eliminate the hidden costs associated with production delays, material waste, and regulatory failures. In 2026, the complexity of global logistics and the tightening of safety mandates mean that a "pretty" design is secondary to a "producible" one. Our DFM framework ensures that your product is optimized for reducing landed cost manufacturing while maintaining 100% adherence to ASTM F963 DFM compliance and EN71 design optimization. This section details how we transform technical engineering into a powerful engine for business growth and brand security.
Designing for Safety Standards:
Compliance by Geometry
Relying on end-of-line inspections to catch safety hazards is a reactive approach that leads to high scrap rates. Our toy safety DFM philosophy is built on "Compliance by Geometry," where safety is engineered directly into the part's DNA.
Mitigating Sharp Edges and Small Parts at the CAD Level
Through EN71 design optimization, we analyze every radius and vertex of a character sculpt. If a design features a cape or a weapon that is too pointed, we adjust the fillet radii to ensure it passes "sharp point" testers without compromising the character's aesthetic. Similarly, we engineer internal locking mechanisms for articulated joints to ensure that "small parts" cannot be detached under tension. This proactive toy safety DFM ensures that your product is inherently compliant with ASTM F963 material safety standards, allowing for a smooth transition through third-party toy lab testing and into global markets.
The 5% Rule:
Cycle Time and Material ROI
Consider the impact of a 5% reduction in injection molding cycle time. By optimizing cooling channels through advanced toy tooling R&D and refining wall thickness, we can shave seconds off every shot. Over a high-volume run, this translates into thousands of hours of machine time saved and a significant reduction in electricity and labor costs. Similarly, a 10% reduction in material waste through hot runner system R&D and "lightweighting" geometry significantly improves your mass production toy ROI. These savings allow IP holders to maintain healthy margins even in inflationary environments, proving that DFM is the ultimate tool for reducing toy production costs.
Lowering Assembly and Logistics Overhead
DFM also focuses on reducing "touch points." By consolidating parts and engineering snap-fit joints that eliminate the need for screws or ultrasonic welding, we lower the total labor cost per unit. Furthermore, by designing parts to nest efficiently, we can reduce the volume of retail-ready packaging, allowing more units to fit into a shipping container. This optimization of the physical footprint is a critical component of reducing landed cost manufacturing in 2026's global supply chain.
Protect Your Margins and Your Brand
Excellence in engineering is the best defense against rising costs. Explore how our proactive DFM process accelerates ROI and guarantees global compliance for your IP.
The DFM Feedback Loop:
Real-Time Refinement
Our DFM process is a living cycle. We utilize real-time data from our audited factory network China to continuously refine the golden sample development process.
Refining the Golden Sample for Maximum Durability
During the initial production run, we monitor the stress points of the molded parts. If a specific joint shows a higher-than-average wear rate, we immediately feed that data back into the DFM loop to reinforce the geometry. This ensures that the high-speed toy manufacturing process evolves to become more robust over time. This feedback loop is what allows Unstoyppable to maintain a "Zero-Recall" reputation for our clients, protecting long-term brand health and consumer trust.